Topic 2 Resources
| Site: | TCOnline |
| Course: | Lifespan Growth & Development (PSYC2314) DUAL CREDIT |
| Book: | Topic 2 Resources |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Thursday, January 1, 2026, 4:19 PM |
Description

Genetics and Prenatal Development
Watch the video Genetics and Prenatal Development respond to the following questions in your notebook while watching.
- What is a gamete?
- What is the name of the male gamete?
- What is the name of the female gamete?
- What is a zygote?
- What is the germinal stage?
- What is the embryonic stage? What happens during this time?
- What is the fetal stage? What happens during this time?
- What are monozygotic twins?
- What are dizygotic twins? What is another name for dizygotic twins?
- How many chromosomes do humans have? How did we get our chromosomes? Which parent determines the gender of the child?
- What are the sex chromosomes for a male?
- What are the sex chromosomes for a female?
- What is a genotype?
- What is a phenotype?
- What do the terms dominant and recessive mean in terms of genetics?
- What is an allele?
- Describe polygenetic traits.
- Describe co-dominant traits.
- What are teratogens?
- Why is folic acid beneficial?
- What is infertility? What are common causes of infertility in males? What are common causes of infertility in females? What are options for couples experiencing infertility?
Punnett Squares
A Punnett square is a representation of the possible genotypes of offspring.
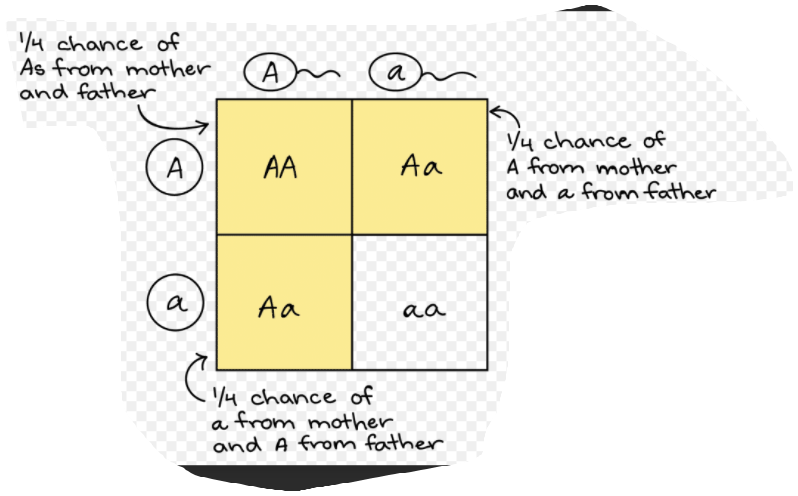
Punnett Square Problem 1
Assume the father is heterozygous brown eyes (Bb) and mother is homozygous blue eyes (bb). Solve the Punnett Square. Determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Punnett Square Problem 2
Assume the father is heterozygous brown eyes and homozygous for straight eyelashes (Bbee). The mother is heterozygous brown eyes and heterozygous for curly eyelashes (BbEe). Solve the Punnett Square. Determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Punnett Square Problem 3
Assume the father is affected with an x-linked recessive trait for colorblindness (X1, Y).
The mother is a carrier (X1, X). Determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period of the Zygote
Watch Period of the Zygote/refer to your text to answer the following questions:
- What occurs during fertilization?
- When is the beginning of the germinal period?
- When is the beginning of the embryonic period?
- When is the beginning of the fetal period?
- What is the age of viability? What does age of viability mean?
Here is the direct link: https://youtu.be/y4HK5CTVkXM?si=fBZ6SxjGwXXMVaxk
Conception to Birth Visualized
In your notebook, describe the process from conception to birth.
Labor
Watch the video Labor and respond to the following questions in your notebook as you watch.
- What are the clues that indicate the beginning of labor?
- What are the three phases of labor? Describe the what does the body does during each phase.
- When is the mother said to be “complete”?
- How long does it typically take a first-time mother to push her baby out?
- What direction is the baby facing in a typical birth?
Pregnancy and Prenatal Care Across Cultures
Watch Pregnancy and Prenatal Care Across Cultures respond to the following in your notebook as you watch.
- Compare and contrast the pregnancies of women in Mexico, Botswana, and the United States.
Here is a direct link: Smart Pearson Player (pearsoncmg.com)
APGAR Newborn Assessment
Watch the video and respond to the following questions in your notebook.
What does APGAR stand for?
A
P
G
A
R
How is the score determined?